Understanding Vibration Transmission Loss in a Mass-Spring System
Calculating the Transmission Loss on a single Mass-Spring Sytem
The Vibration Transmission Loss for a one degree of freedom system is calculated by modeling it as a damped mass-spring system. The ratio between the exciting force and the transmitted force is given by the following formula:
Calculating the Resonance Frequency a damped system
The resonance frequency (fp) in Hz is calculated considering a damped system as shown below:
where:
- f0: Resonance frequency of the undamped system (Hz)
- ξ (xi): Damping ratio
- ω0: Angular frequency of the undamped system
Calculating the Transmission Loss on a Double Mass-Spring Sytem
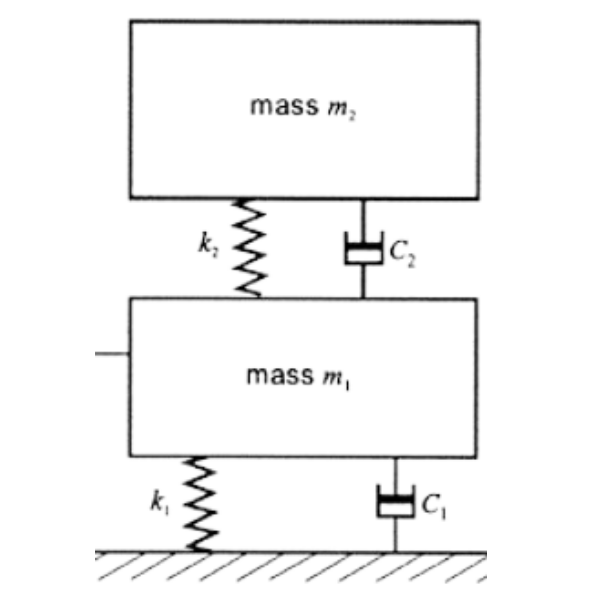
In the double suspension system, the model consists of two masses and two springs connected to a rigid ground. The calculation of the transmissibility is derived from Bies - Engineering Noise Control Theory and Practice using the following formula:
where:
- k1, k2: Stiffness values of springs in system 1 and 2, respectively
- m1, m2: Mass values in system 1 and 2, respectively
- C1, C2: Damping coefficients for systems 1 and 2
In this case, the force is applied on the system 2.
The indices 1 and 2 refer to the components of the system, with index 1 representing the mass, stiffness, and damping connected to the ground, and index 2 representing the mass, stiffness, and damping above system 1.
The two resonant frequencies are calculated using the method outlined in Harris' Shock and Vibration Handbook - Fifth Edition, P1.10.
For more detailed information, read our article on effective vibration reduction strategies.